Technology
Devanagari literacy increases functional connectivity between acoustic-phonetic, graphomotor brain areas: Study
Hyderabad, Nov 26
In a finding that throws more light on the human brain's capabilities, a study by University of Hyderabad (UoH) researchers and others, has found that the usage of Indian scripts, specifically Devanagari, influences brain networks relevant for speech and attention differently as compared to alphabetic scripts like English.
The research paper titled How does literacy affect speech processing? Not by enhancing cortical responses to speech, but by promoting connectivity of acoustic-phonetic and graphomotor cortices by Prof. Ramesh Mishra, Head, Centre for Neural and Cognitive Sciences, University of Hyderabad (UoH) and others has been published in the prestigious Journal of Neuroscience.
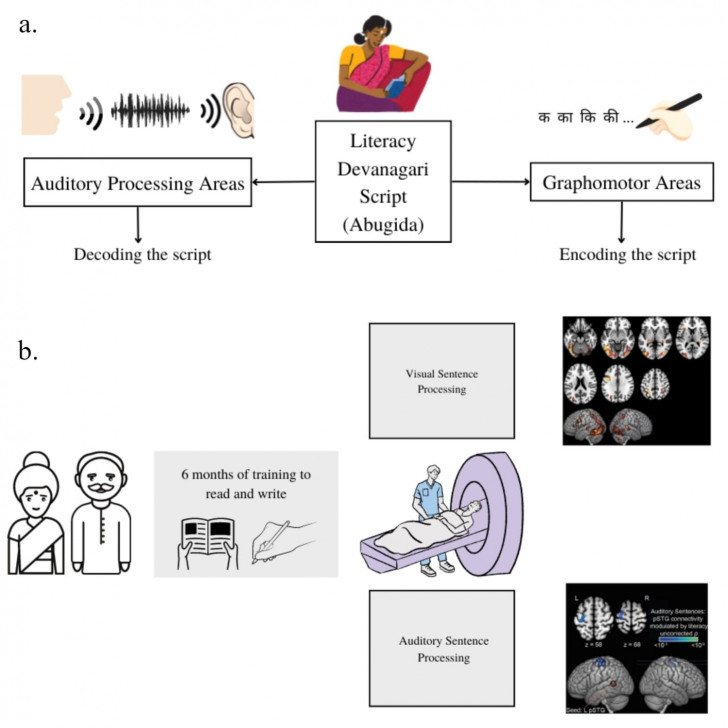
Literacy has far-fetched consequences to how our brains respond to speech. However, script specific effects on neurobiology modifies earlier ideas where cultural differences were ignored.
As part of the study, 91 Hindi speaking participants with varying literacy levels participated in an fMRI study. Twenty-two illiterate participants were trained to read and write Hindi over six months following which they participated in visual and auditory sentence processing tasks. Contrary to existing evidence that highlights the role of literacy in modifying how we process speech; the results suggest that such an impact of literacy cannot be generalised across different scripts, a UoH's release stated.
The findings also indicate that literacy enhanced functional connectivity between auditory processing areas and graphomotor areas in the brain.
This implies significant coupling between hand-motor regions (writing) and auditory processing areas while the participants processed sentences. "Thus, the potential role of writing cannot be ignored while we explore the role of literacy on speech processing," the researchers point out.



































