Headlines
MP researchers’ incisionless device to boost treatment for diabetes, obesity
New Delhi, Jan 22
A team of an international team of researchers, led by those from India’s Madhya Pradesh, has developed a completely incisionless device that replicates metabolic surgery without making any cuts and could surpass current technologies for managing conditions such as severe obesity, Type 2 diabetes, and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH).
The researchers found that the ForePass endoscopic showed extraordinary efficacy in treating these metabolic conditions, providing unmatched treatment for millions of people who reject invasive surgery or do not respond to drugs.
"The ForePass device will be a game-changer for treating severe metabolic conditions. It replicates the effects of metabolic surgery without invasive procedures and without making any cuts to internal organs. It's the first device of its kind and will pave the way for a new era in managing severe metabolic conditions," said lead author Dr. Manoel Galvao Neto, endoscopic surgeon and researcher based at Sri Aurobindo Medical College, in Madhya Pradesh.
"It is a crucial development, as only 1 per cent of patients opt for bariatric surgery due to its invasive nature. The medical community is eagerly anticipating the upcoming clinical trials involving the ForePass device," Dr. Neto added.
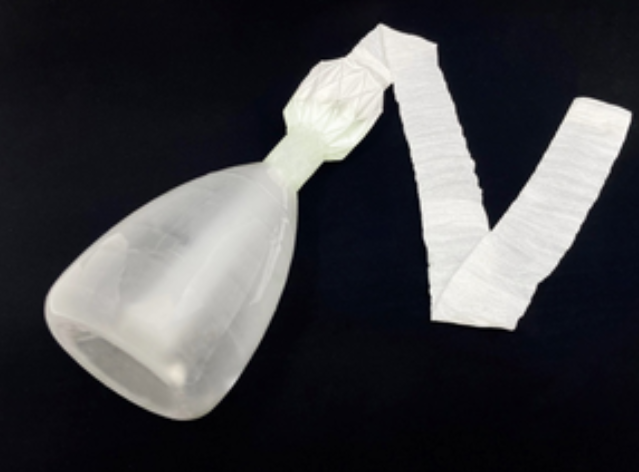
ForePass is an innovative device, developed by Keyron, that combines a gastric balloon crossed by a central channel that connects to a flexible intestinal sleeve, thereby effectively replicating the mechanism of invasive metabolic surgery without the need for surgery or making any incisions.
The device is inserted into the stomach and initial tract of the small intestine using endoscopy, a much less invasive and cheaper procedure compared to metabolic surgery. Unlike metabolic surgery, ForePass is fully reversible, making it an appealing option for patients.
The team evaluated the ForePass device's impact on weight, insulin sensitivity, and faecal microbiota (a range of microorganisms) in pigs.
The results, published in the journal Gut, revealed a 79 per cent reduction in weight gain compared to the control group, suggesting it may be substantially more effective than common metabolic surgeries like gastric bypass. It also showed substantial improvements in how the body handles insulin and reduces glucose in the liver compared to controls.
The study found markedly improved response to insulin, enhanced use of glucose, and beneficial changes in metabolic health-related gut bacteria.
The device also favourably altered faecal microbiota, boosting bacteria linked to metabolic well-being. These outcomes align with a reversal of severe obesity, diabetes, and MASH, indicating an overall improvement in metabolic health.
Keyron plans to initiate human clinical trials for ForePass, which is anticipated to start in early 2025.

59 seconds ago
Bayern survive Union scare in five-goal DFB Cup thriller

2 minutes ago
Arsenal beat Brentford, Leeds stuns Chelsea in Premier League

3 minutes ago
Privilege to have that kind of confidence from management: Gaikwad on batting at No. 4

4 minutes ago
1st Test: Rachin, Latham's tons help NZ take 481-run lead over WI at stumps on Day 3

4 minutes ago
Meet Deeya Yadav, who makes historic WPL entry, to play alongside Shafali Verma

9 minutes ago
Rupali Ganguly pens note for ‘man who creates stars’ Rajan Shahi on his b'day

10 minutes ago
Mahhi Vij: I’ve always believed in karma

11 minutes ago
Deepika Padukone, Ranveer Singh are a timeless power couple, says Orry

12 minutes ago
Big B requests cricket coach Amol Mazumdar to let team have pizza post win

13 minutes ago
Raj Nidimoru's ex-wife says ‘not looking for attention, sympathy’ post his wedding to Samantha

14 minutes ago
Randeep Hooda wades into Tiger’s water: There is no greater joy

15 minutes ago
Priyanka Chopra to husband Nick Jonas: ‘Cementing’ your legacy in Hollywood was a proud moment for me

16 minutes ago
Samsung hints new Exynos chip for Galaxy S26, shares 125 patents with smaller firms






















